When it comes to manufacturing plastic parts, businesses often face the choice of thermoforming vs injection molding. Both methods are widely used in industries ranging from packaging and automotive to medical devices and consumer goods. While injection molding is similar to thermoforming in that both shape heated plastic into functional products, they differ greatly in terms of cost, speed, design capabilities, and production volumes.
Understanding these differences is essential for choosing the right process for your project. Let’s take a closer look at what thermoforming and injection molding are, and then compare their strengths and weaknesses.
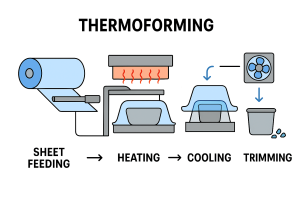
Thermoforming is a process where a sheet of plastic is heated until pliable, then pressed against a mold using vacuum or pressure. After cooling, the plastic takes the shape of the mold and is trimmed into its final form. Thermoforming is often chosen for larger parts, low-volume runs, and prototypes. Common applications include bathtubs, trays, packaging, displays, and automotive panels.
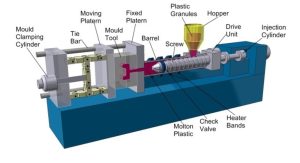
Injection molding works differently. Plastic pellets are heated to a molten state and then injected under high pressure into a steel or aluminum mold with one or multiple cavities. Once cooled, the parts are ejected and ready for use. This process is ideal for high-volume, highly detailed products such as gears, bottle caps, medical components, and consumer electronics.
Thermoforming: Uses heated plastic sheets and single-sided molds. Easier to modify and faster for prototyping.
Injection Molding: Uses molten pellets injected into multi-cavity molds. Highly automated and suitable for complex, detailed parts.
Thermoforming: Best for simpler designs with moderate detail.
Injection Molding: Capable of producing very small, intricate, and precise parts with consistent quality.
Thermoforming: One part is made per cycle. Good for small production runs and prototypes.
Injection Molding: Can produce thousands of parts per cycle thanks to multi-cavity molds. Perfect for large-scale manufacturing.
Thermoforming: Generates more scrap, since excess sheet material must be trimmed away.
Injection Molding: Minimal waste, as molten plastic fills the mold directly.
Thermoforming: Lower tooling costs and faster setup. Ideal for startups or short-term projects.
Injection Molding: High upfront tooling investment, but cost-effective at scale due to low per-unit cost.
Thermoforming: Produces good finishes but with looser tolerances.
Injection Molding: Delivers excellent surface quality and tight dimensional tolerances, ideal for precision products.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
When comparing thermoforming vs injection molding, the right choice depends on your project’s needs:
Choose thermoforming if you need large parts, low-volume production, quick prototypes, or want to minimize tooling investment.
Choose injection molding if your project requires high-volume output, precision, complex designs, or long-term cost efficiency.
Ultimately, both processes play a vital role in modern manufacturing. Since injection molding is similar to thermoforming in its goal—shaping plastics into useful products—the key difference lies in scale, complexity, and budget. Understanding these distinctions ensures that you select the best manufacturing method for your business.
Previous: How Does Plastic Extrusion Work?
Next article: The Materials of Using in Thermoforming Machine